Key Highlights:
- Business Potential
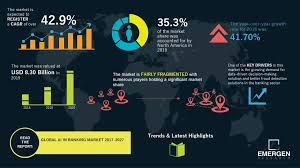
- McKinsey & Company projects that successful AI implementation could boost banks’ annual operating profits by £200bn to £340bn.
- However, many institutions struggle with practical execution due to data fragmentation and lack of a Single Source of Truth (SSOT).

- Implementation Approach
- The article recommends a measured, phased transformation strategy
- Likens modernizing banking systems to steering an oil tanker – requiring careful, systematic changes
- Emphasizes the importance of rebuilding architecture component by component
- AI Applications in Banking
- Loan and mortgage approvals (subject to strict regulatory compliance)
- Customer service enhancement
- Data testing, reconciliation, and cleaning
- Code generation for data platforms

- Regulatory Considerations
- E
 U AI Act classifies specific AI systems (like loan approval) as “high-risk”
U AI Act classifies specific AI systems (like loan approval) as “high-risk” - Requires robust risk management, data governance, and technical documentation
- Emphasizes human oversight and transparency
- Key Challenges
- Data management and consolidation
- Cultural change within organizations
- Building and maintaining customer trust
- Balancing innovation with security

- Strategic Recommendations
- Establish AI governance boards
- Implement comprehensive training programs
- Focus on data quality and management
- Prioritize customer-centric approaches
The article concludes that the future of banking technology depends on developing resilient AI systems that can adapt to changing conditions while maintaining robust security and delivering innovative services.
Technological Foundations

Key Technological Drivers
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Primary transformative technology in banking
- Potential to boost annual operating profits by £200bn-£340bn
- Applications spanning multiple operational domains
- Data Architecture
- Shift towards integrated data strategies
- Development of Single Source of Truth (SSOT)
- Consolidation of disparate data systems
- Open Banking Technologies
- API-driven data sharing
- Secure third-party data collaboration
- Enhanced competition and innovation

Implementation Strategies
Methodical Transformation Approach
- Phased Implementation
- Incremental system modernization
- Controlled, bite-sized architectural changes
- Minimizing operational disruption
- Governance Frameworks
- Establishment of AI governance boards
- Comprehensive oversight mechanisms
- Rigorous use case evaluation

Technological Implementation Methods
- Strategic AI Integration
- Targeted application in specific domains
- Loan and mortgage approval processes
- Customer service enhancement
- Operational efficiency improvements
- Data Management Techniques
- Advanced data cleaning and reconciliation
- Automated code generation
- Standardized data formats
- Real-time authentication protocols

Challenges and Considerations
Regulatory Landscape
- Compliance Requirements
- EU AI Act regulations
- High-risk system classifications
- Mandatory technical documentation
- Robust risk management protocols
Organizational Challenges

- Cultural Transformation
- Managing human-technology interface
- Comprehensive staff training
- Developing AI literacy
- Technical Complexities
- Consolidating fragmented data systems
- Maintaining data quality
- Ensuring system interoperability
Trust and Security Imperatives

- Balancing innovation with robust security measures
- Transparent AI system operations
- Maintaining customer confidence
- Protecting sensitive financial data
Future Outlook
Key Strategic Priorities
- Develop adaptive, resilient AI systems
- Prioritize customer-centric technological solutions
- Continuous operational modernization
- Seamless integration of advanced technologies
Emerging Technological Trends
- AI-powered customer interaction platforms
- Enhanced predictive analytics
- Automated compliance and risk management
- Personalized financial solutions
Maxthon
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
Maxthon private browser for online privacyThis meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.
